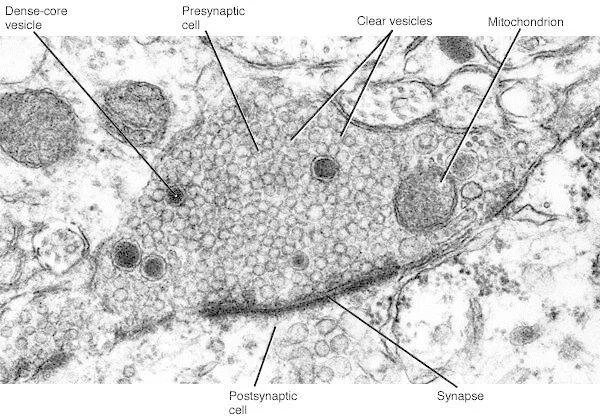
Answer: Botulinum toxin inhibits the molecular machinery at acetylcholine terminals at the neuromuscular junction.
Botulinum toxin is a potent neurotoxin that is produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum. Although uncontrolled exposure can be lethal, it can be used clinically as a treatment for spasticity, strabismus, or chronic migraines. It is best known for being used cosmetically to remove facial wrinkles.
When botulinum toxin enters the system, it is taken into the terminals of acetylcholine producing nerves. Once inside, it interferes with the molecular machinery necessary for vesicle fusion and synaptic release. In particular, it cleaves SNARE proteins such as VAMP/synaptobrevin, SNAP-25, and syntaxin. Without these proteins, the neuron is unable to release neurotransmitter, which results in a loss of cholinergic tone onto the muscle. Because acetylcholine is the primary neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction, paralysis is a consequence of a loss of acetylcholine acting at the muscle.
Exposure to botulinum toxin can result in symptoms such as weakness of the facial muscles. Severe cases of exposure may result in a spreading of that weakness to the upper body, and potentially even to the lungs and diaphragm. This may be lethal. Common tests performed at the hospital to evaluate botulinum poisoning include a brain scan or an examination of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Clostridium botulinum is an anaerobic rod type bacterium that is often found in soil and plants, as well as inside the digestive systems of several animals. It can produce 8 different types of toxins, which are labeled by letter: A, B, C1, C2, D, E, F, and G.
Botulinum toxin-A is the most toxic, and is usually the culprit in cases of botulism toxicity in humans. The A serotype is commercially available for use in cosmetics. The two main types of preparations go by the brand names Dysport and Botox. It is estimated that Botox is three times more potent than Dysport (A double blind, randomised, parallel group study to investigate the dose equivalence of Dysport and Botox in the treatment of cervical dystonia.)
Type B is highly potent, and is also associated with human cases of botulinum poisoning. It is not currently approved for use cosmetically. A preparation has been isolated under the name Neurobloc.